Row Level Security Capability was introduced with 2016 version SQL Server. Same is available in Azure SQL Database also as of today. This blog will detail a novice example on how to implement.
This is the planned implementation flow:
- About the example
- Prepare Sample data
- Create Predicate function
- Apply Security Policy
- Test Security
1. Plot
For the purpose of example, we will take the case of an imaginary Super market. Let us assume there are Supervisors assigned to each department in the shop and we want each supervisor to see only items he is responsible for.
RLS is applied on tables but in this example we will apply to a VIEW, which makes more sense as it is close to the real world scenarios.
2. Prepare sample data
Find the schema and sample data I used for the example:
Table: dbo.Employee
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Employee](
[EmpID] [int] NULL,
[Department] [varchar](50) NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](150) NULL,
[Username] [varchar](50) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
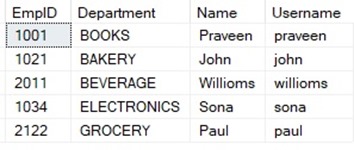
Table: dbo.StockByDepartment
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[StockByDepartment](
[Department] [varchar](50) NULL,
[Item] [nvarchar](100) NULL,
[UnitPrice] [money] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
![Screenshot[2] Screenshot[2]](https://blog.ninethsense.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Screenshot2_thumb.jpg)
View: dbo.Stock
CREATE VIEW [dbo].[Stock]
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
SELECT e.Department, e.EmpID, e.Name, e.Username, d.Item, d.UnitPrice FROM dbo.StockByDepartment d
INNER JOIN dbo.Employee e
ON d.Department=e.Department
![Screenshot[3] Screenshot[3]](https://blog.ninethsense.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Screenshot3_thumb.jpg)
3. Create Predicate function
Run this script to create predicate function over dbo.Stock view.
CREATE FUNCTION fn_SecurityPredicate(@username sysname)
RETURNS TABLE
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
RETURN SELECT 1 AS [fn_SecurityPredicate_result]
FROM
dbo.Stock
WHERE
@username=USER_NAME();
4. Apply Security Policy
Run this script to apply security policy over dbo.Stock view
CREATE SECURITY POLICY DepartmentFilter
ADD FILTER PREDICATE dbo.fn_SecurityPredicate(Username)
ON dbo.Stock
5. Test Security
Now it is time for us to try out the applied security with various users.
Create sample users with the name you have provided in “Login” field of dbo.Employee table, and login to SSMS using it and try SELECTing the records in dbo.Stock.
For demo purpose, below code will create some sample users and grant permission to dbo.Stock view:
CREATE User paul WITHOUT LOGIN
GRANT SELECT on dbo.Stock TO paul
Now, for the sake of testing, you can use the below code:
EXECUTE('SELECT * FROM dbo.Stock') as USER='paul'
You should see filtered data like the one below:
![Screenshot[4] Screenshot[4]](https://blog.ninethsense.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Screenshot4_thumb.jpg)